Best Content, Internal Linking, A Horrifying Google SERP, & More!
What Content Performs Best for Getting Links: A Study
This is an interesting, but far from scientifically rigorous study on what kind of content gets links. Perhaps the most interesting thing about this is how it could be replicated within the niches that matter most to you, since it is more art than science (but, I would argue, still gives you a solid 80/20 of what content does well in your niche and why).
I manually analysed with my eyes the “top” (as defined by Trust Flow and Citation Flow) 100ish links for 2 random well ranking sites in Insurance, Ecom in an interesting niche, Ecom in a dry niche, Travel and Finance. I only really cared about links that looked, to me, to have been strategically built through the active creation and distribution of a thing. That thing can be as involved as huge scale video production, right to a simple Tweet sharing a quote with a journalist. I ignored links that looked, to me, to have occurred entirely naturally such as genuine forum discussions, certain reviews and so on. I did this because I am interested primarily in understanding what strategies are most effective in order to ensure I am doing the best shit now, and for the future.
This is a long, thoughtful piece that I’d highly recommend reading through. The author goes through what kinds of content were most “paid for,” what kind of content got the best (most authoritative) links, and what content got the flat-out most links:

A Brief Content Study of Things You Probably Already Knew
This classic Backlinko style post ticks all the boxes:
✅analyzes an absurd amount of data
✅partners with a best-in-class big business
✅lots of numbers and statistics
✅more than 50% of the content on the page is comments
Classic.
The post itself is quality, but mainly serves to back up common SEOisms with data generated from articles in Buzzsumo’s database, such as:
- Most articles generate zero backlinks
- Long content generates more backlinks than shorter content
This post is probably of most interest if your site relies on social media more so than backlinks, but if that’s the case, you probably knew most of this anyway…
Why Google Doesn’t Use CTR and E-A-T Like You Think
An SEO think-piece (rant) on how many SEOs are full of shit and correlation does not imply causation, and how, with cherry-picked data, some SEOs spread misinformation that refuses to die because it gets caught in viral feedback loop.

Google does NOT use E-A-T as a ranking signal.
It doesn’t matter how often Googlers reject that belief. It doesn’t matter how much they debunk it. The same people come back time and again and proclaim their correctness, asserting they finally have proof that the E-A-T- Fairy is real and bestowing blessings upon everyone.
Wikipedia alone proves there is no E-A-T ranking signal. Wikipedia is not only NOT an expert Website, the news media has published many stories about subject-matter experts being driven away from Wikipedia. Although Wikipedia’s community has responded to these criticisms and attempted to adjust their policies through the years to promote better editing, their fundamental principle of allowing consensus from the unwashed masses to make decisions has led to many potentially good articles being edited into mediocrity. In some cases outright false information persists in Wikipedia articles because their rules against “edit wars” favor the people who are clever enough to revert accurate corrections.
You’ll most likely have a strong reaction to this post–whether for or against, but that’s a good thing. On the one hand, it’s important to try and validate on your own the kinds of things some very visible SEOs claim. On the other, Google has zero interest in having any of us really understand their algorithms work (outside of making sure they can be easily crawled for maximum indexing and scraping, but that’s a story of another day).
So, I mean, you’ve got to accept SOME advice eventually. Probably helpful to read something from both sides of the SEO aisle as much as possible. For every Marie Haynes theory read something from Michael Martinez.
Then start drinking…
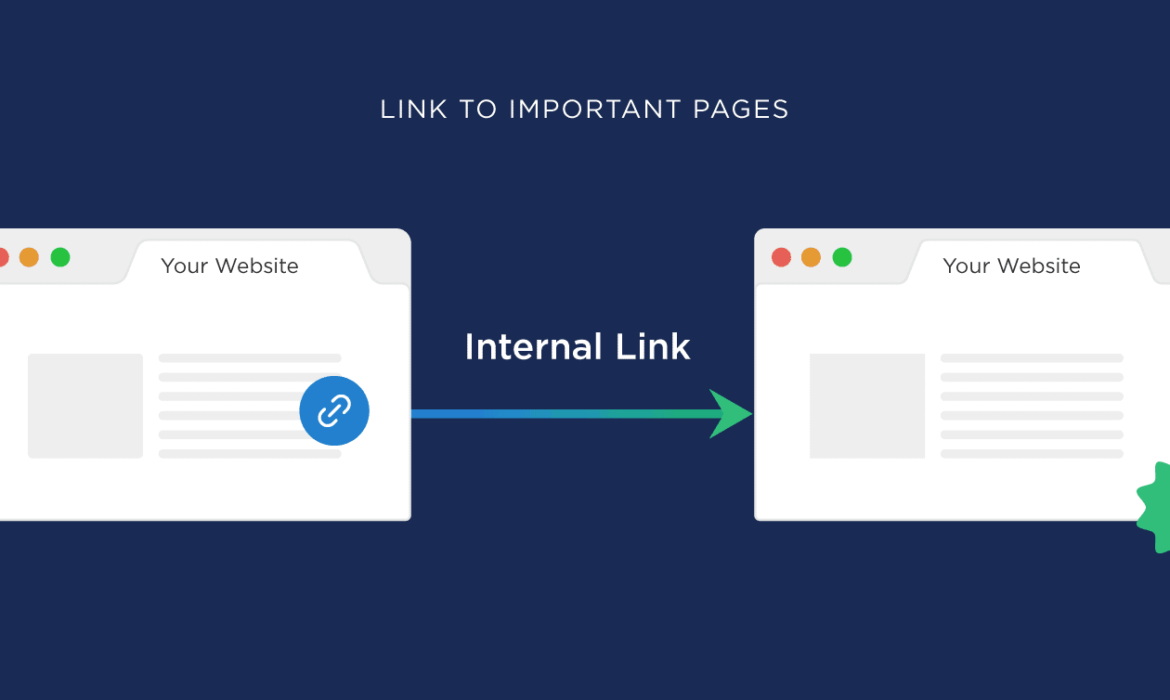
Decentralized vs Centralized Internal Linking
https://www.kevin-indig.com/the-best-internal-linking-structure-depends-on-your-business-model/
Interesting post from a really smart SEO about the two main ways you can approach internal linking. A bit of an advanced post, but one you shouldn’t miss.

Websites vary by the point of conversion, depending on what business model they follow. One type of site leads all users to one or a few landing pages, the other has users sign up on almost every page. Should the approach to internal link optimization be the same for both? Of course, not!
Sites that have a few points of conversion are what I call “centralized”. They don’t have scalable page templates, in most cases. Instead, they consist of landing pages, a blog, and some other pages. Centralized sites are often used by SaaS, app, and enterprise companies like Atlassian, UBER, or Salesforce.
The opposite is sites with many points of conversion, used by Ecommerce businesses, social networks, and marketplaces. They are “decentralized” sites with page templates they can scale, such as public instances, user profiles, apartment listings, products, or categories. Examples are Pinterest, Airbnb, and Amazon.
The Definitive Guide to Internal Links for SEO
Backlinks are the backbone of ranking in Google. There’s an army of SEOs spending tens of thousands of dollars on acquiring backlinks every single month.
Everyone knows this but most SEOs overlook the power of strategic internal linking.
Internal links are just as important and best of all, they’re free.
What if I told you that instead of launching yet another guest posting campaign for a page that is stuck in the third position, you could use internal links to work your way to the top?
That’s exactly what you’re going to learn today.
How Links Work
Your website’s homepage is almost always going to be the strongest page.
It likely gets the most visitors and attracts the most backlinks.
Well, Google discovers the web through links and that’s why backlinks are valuable in the first place.
The same logic applies to internal links.
Let’s pretend the homepage is worth 100 points and has links to ten other pages on your site.
Assuming they have no external links to them and no other internal links, they would in theory carry a value of 10 points.
If you now link to another 10 pages from any of those, they would have a value of 1 point each.
The Value of Internal Links
Here are just a few reasons both Google and your users need internal links:
- Provide navigation options for both users and search spiders
- Via the anchor text, they tell them what a page is about (e.g. topic)
- Pass “link power” to other pages, indicating their importance
- Help understand which pages are related to each other
Internal links are critical for ranking. Look at any successful site and I can guarantee they’re heavily linking to their other content pages.

(Source: Author’s screenshot)
Internal links are also split into two categories. Contextual links are more powerful and are present in your main content (e.g. the majority of examples in the example above) and then there are navigational internal links (the box on the right side).
These strategies are best used to:
- Boost up pages that are close to the top 3
- Funnel link juice to pages that don’t attract many links (e.g. product pages)
- Help Google index new pages faster and give them a quick boost
Now let’s get into how to actually implement internal links on your own site for a nice ranking boost to your most important pages.
A word of warning: As with anything, you don’t want to go crazy with this. Just because these strategies work, doesn’t mean you’re going to want to link out with every single word in an article. Keep the user in mind and use common sense.
5 Internal Linking Strategies That You Can Use Today
1. Keep Valuable Pages Close to Your Homepage
With your homepage likely being the strongest page and passing the most value, you want to keep your most important pages as close to it as possible.
This means that whether you’re trying to rank a service page or a comprehensive guide on your blog, you’ll want to feature it either in your menu, sidebar, footer, or homepage.
Here are some of the most effective ways we’ve done it:
- Use comprehensive, layered dropdown menus
- Use your footer as a “mini sitemap”
- Have long-form pages – more words means more linking opportunities
2. Build Links From Your Top Pages
We get it. Sometimes a page is important but not necessarily a great fit for your homepage or your main menus.
In this case, you can make use of other high authority pages on your site.
You can use a tool such as Ahrefs to determine the highest value pages on your site by clicking on either “Top Pages” for highest traffic pages or “Best by Links” for the pages with the most backlinks.

(Source: Author’s screenshot)
Both of these will include super important pages on your site.
Go through all of the most notable pages in these categories and try to look for opportunities to link to the pages you’re trying to rank.
If there is no “natural way” there already, you can modify the content to make it work.
As a simple example, you could do something like:
“If you’ve enjoyed reading this guide, you can also check out our 7-chapter image SEO guide.”
Get creative and combine search engine optimization with providing value for your users.
3. Create Internal Links From Relevant Pages
Once you’ve been through the strongest pages on your site, the authority site is covered.
Now it’s time to focus on relevance.
Do a Google search with “site:yourdomain.com YOUR TARGET KEYWORD” to see what other pages Google deems most relevant to that topic.
Go through these pages and ensure they also link to your target page.
4. Use a Related Posts Plugin
For WordPress sites, there are plugins out there that show users “related posts” after each article. Not only will these help you decrease bounce rates and help users stay on your site longer, these also count as internal links and can help with rankings.
You’ll want to ensure these plugins are configured properly and only show posts that are actually related, not just a random shuffle.
Another thing to note here is that some of the more common plugins for this slow down your site massively, an example of this is the “Yet Another Related Posts Plugin”.
The plugin that we use and recommend is Related Posts for WordPress.
It’s fast and allows for great customization.
5. Do a Scan for Orphan Pages
Orphan pages are a common issue with bigger sites. These are pages that exist on your site but don’t have any internal links pointing to them. This means Google probably won’t find them and neither will your users.
You can find these pages on your site with most SEO auditing software.
We like to use Screaming Frog SEO Spider.
They have a free version that is more than enough for most people and it is also blazing fast.
Plug in your domain, have it scan your site, and then sort it by the number of “inlinks” to find pages with no internal links to them.
You can also use the tool to review your site structure and get an overview of how many pages have a click-depth (how many clicks it takes to get to a page from the homepage) of 3 or more and try to bring them closer using internal links.
Tools to Help Manage Internal Links
This FREE Excel Template
For smaller sites, we like to keep an Excel sheet with every single page on the site, where the internal links go to, and what anchor text they use.
This gives you a nice overview of where you might be erring on the side of over-optimization.
It also helps keep things future proof. One day you might delete a page and even though you’d redirect it after, you don’t want other pages to link to it anymore.
This keeps a nice and organized directory you can reference at any time.
Yoast SEO Premium Plugin
Yoast’s SEO plugin is one of the most common solutions for WordPress SEO and for a good reason. It’s simple to use and it covers most of your bases.
By upgrading to their premium version ($89 one time fee), you also get access to their internal linking tool.
This lists the most prominent words on a page and automatically gives you recommendations on pages on your site these could link to.
It’s semi-automated and provides highly relevant results.
Not only that, they also give you a nice and convenient overview of how many internal pages an article links to and how many they have coming in.
FAQ
What Anchor Text Should I Use for Internal Links?
The anchor text is the clickable part of a link that your users can see.
It’s how users know what to expect from a link and it tells Google what the page is about.
Although over-optimization of anchor texts is something that can hurt your rankings with external links, they are a bit more lenient when it comes to internal links.
Still, you don’t want to overdo it. Make it easy for the readers and try to include a keyword or two when it makes sense.
Should I Ever Nofollow Internal Links?
The nofollow tag tells Google to not pass any “link value“ when it is present. You’ll often see people use this for either paid links or affiliate links.
Although it’s best practice to not use them on your own site, there are some instances where this is OK.
Warning: Do not mess around with nofollowing links unless you know what you’re doing and have some SEO experience. It’s easy to do some damage with them.
If you have pages such as a members area or login page, it’s best to nofollow links to these, especially from major places such as the header.
How Many Links Should You Have Per Page?
Okay, so internal links clearly have a ton of power and can help you rank.
When we’ve told our clients about this strategy, some of them have gone bonkers and started linking out with almost every other word on a page.
Don’t.
Google’s webmaster guidelines say that a page should have a “reasonable amount of links”
According to Google’s Matt Cutt’s, around 100 is a safe number. This is the total number of links on a page – internal, external, navigation, and the whole nine yards.
Now, keep in mind that this does (generally) not mean that if you have more than 100 links you’re going to lose rankings and traffic.
This simply means that beyond a hundred, each link carries less weight.
The Ultimate SEO Guide to Image Optimization
Get your on-page in order. Optimize the titles, write unique meta descriptions, ensure you’re using all your keywords, and optimize your images.“
I’m sure you’ve heard this a million times.
Well, how the heck do you do it? What is image optimization and how does it work?
That’s what you’re going to learn today.
The Basics
“A picture is worth a thousand words.”
The old English proverb is more true than ever when it comes to digital content.
No one wants to read through a 5,000-word guide that is simply a wall of text.
Images are great for illustrating your points, explaining complex concepts, or just entertainment value.
*Insert silly meme*
We probably don’t have to convince you to start using images in your content as the benefits are obvious.
Just one small issue…
Google cannot see images the way we do and thus generally have no idea what’s on them.
That’s why we need image optimization.
(Editors Note: Thanks to AI and machine learning, Google now does have technology that can understand images. However, the accuracy is nowhere close to where it needs to be so the following is still critical for optimal results.)

Here are the key ways we can optimize images:
Table of Contents [show]
Optimizing Images With Text
There are some super easy ways to give Google (and your visitors) additional context about your images. These help you rank better in Google Images and also create additional keyword relevance for the pages you have the images on.
Alt Tags and Title Tags
The HTML “alt” attribute is the alternate text for an image in the event that it cannot be displayed. This could be due to a browser configuration, accessibility reasons (e.g. blind users), or other technical faults.
It allows the user to understand what the image would’ve been about.
Tech has gotten far enough where images not loading aren’t a major concern so users don’t have a lot to benefit from this but search engines use it as a way to understand what the image is about.
The tag is implemented within the image as such:
<img src=”optimizing-images-for-search-engines.png” alt=”How to create proper alt text for images” />
The image title tag is another way to tell Google what your image is about. It’s also what you see when you hover over an image for more than two seconds.
It’s best practice for this to be slightly different than the alt text as this may allow you to target more keywords.
What Do You Write as the Alt Text?
You’ll want to write 3-7 words describing the image and using a relevant keyword within that.
Please note that this should NOT be the main keyword of your post, but one relevant to the image. You also do NOT want to stuff this full of keywords.
“Image SEO guide – optimizing images” is not okay.
Let’s use an SEO-related example here.
Pretend we have an article about keyword research.
The first image will likely be the “header” image with the blog post title and it’d be great to add the alt text of that as something that contains your main keyword “The Ultimate Guide to Keyword Research“.
Next up we’ll have a photo of us analyzing some keywords in a section of the article about buyer intent. We might set the alt text to “How to use Ahrefs to identify buyer intent keywords”
And so on and so forth.
Each image is supposed to supplement the content around it and the alt text supports those long-tail keywords and topics.
Optimizing Image File Names
File names are just another way of letting Google know what the image is about.
As per their Webmaster Guidelines:
“The filename can give Google clues about the subject matter of the image. For example, my-new-black-kitten.jpg is better than IMG00023.JPG.”
Keep it simple, utilize keywords, and keep them short.
Generally, we keep all three – alt tags, titles, and the file name – quite similar and rewritten versions of each other.
Surrounding Text
The content around your image is a great indication of what it is about.
If your file name, alt text, and title indicate that the image is about SEO but the surrounding text is about the best restaurants in New York – what do you reckon Google is going to think?
This is a great tactic to utilize to rank in Google Images.
We had a client who was ranking number one with a “blood sugar chart” and raking in tens of thousands of visitors a month just from one image that was well optimized for that exact term.
Captions

Captions are generally the best example of “surrounding text” for images but here’s one place where we urge you to actually ignore search engines.
Sure, having a keyword in there would be great but captions are one of the best ways to try and engage with your readers.
Get creative and toss a joke in there instead.
Image Speed Optimizations
Images are one of the biggest contributors to how long your website takes to load.
Site speed is not only an important ranking factor but it is also critical for conversions.
According to Kissmetrics, a 1-second delay in page response can result in a 7% reduction in conversions.
The Best Image Size for Blog Posts
Even though my computer runs at a high resolution and I have a big 32-inch screen, websites generally load a lot smaller than that.
As you can see on the image below – the total width of my screen is 2670 pixels but the content from our blog is only displayed across 770 for the sake of people with smaller screens as well as readability.

The same goes for images. Since our blog can only display things at a maximum width of 770 pixels, we should resize every image larger than that before uploading it.
Otherwise, we might upload an image that’s 4,000 pixels wide and has a file size of 5,3 MB. Not only will it take a lot longer to load for the user but your CMS will have to change the display to 770 pixels anyway.
Resizing your images to the size they’re actually going to be displayed at is one of the best ways to increase your site speed.
The Best Image File Formats for Web
The three most common file types for saving images are JPEG, PNG, and GIF, and the file size differences them can be huge.
Here’s an example:

As you can see, the comparative file size differences are quite significant and they can be even bigger depending on the image type. You’ll also notice small quality differences.
So which one should you use?
Here’s the mini reference list we use for our team.
Pros and Cons of JPEG Images
- The best option for photos (e.g. stock, social media, etc)
- Three compression options for quality
- Great color quality
- Generally smallest file sizes
Pros and Cons of PNG Images
- Allows transparent backgrounds and shadows
- Highest quality images
- Good for small images
- File size can be a bit bigger
Pros and Cons of GIF Images
- Allows animations
- Transparent backgrounds
- Lower color quality
- Small file sizes
Use Image Compression
There’s software out to compress images and reduce their file size. Here’s an example of what happens:

There’s a 29.2% reduction in file size and I cannot see any difference in the quality.
Now imagine the impact of this on-page speed if you do it for 25 images in a long guide.
It’s massive.
There’s a software called ImageOptim for Mac, which is what we use, and it lets you compress images within seconds.
If you’re a Windows user, we can recommend an online tool such as ShortPixel.
Compress your images, folks.
Utilize Responsive Images
As discussed earlier, in spite of what size images are displayed at, they generally have to be loaded at the full size first.
Meaning that if your blog is 770 pixels wide like ours and you have an image with the same width, but someone views it on mobile at 240 pixels, they have to wait for the whole thing to load.
Responsive images take care of this by automatically creating small, medium, and large versions of an image.
Some content management systems, such as WordPress, take care of this automatically.
If you’re using another CMS, you’ll want to find an extension or plugin that allows you to do the same.
Additional Optimizations
Structured Data
Structured data was created to standardize common information about online content.
Ever notice that when you Google for recipes, it might provide you with the cooking time and nutrient information? Or when Googling for reviews, you’ll see little stars for the ratings?
That’s structured data.

In terms of structured data for Google Images, there are currently three main options:
Videos – Optimize the thumbnail image, modify the duration, list views, etc.
Recipes – Choose the image displayed in search results, add user ratings, cooking time, nutrition information, preparation time, and more.
Products – Add product images, list prices, availability, and reviews.
Twitter Cards and OpenGraph
Using the OpenGraph protocol and Twitter Cards allows you to choose the image that is displayed on social media when a page is shared:

Although these do not have a direct impact on SEO, having a custom image will help you appear more appealing and can lead to higher traffic and thus, more links.
If you’re a WordPress user, this is super easy to do with the Yoast SEO plugin by going to the “Social” section. For the Shopify folks out there – check out this guide on the Shopify blog.
Valuable Content in Images
One common mistake we’ve seen dozens of our clients make is putting important content on images.
There are a lot of designers out there that know nothing about SEO and how search engines work and they may design your site in a way where critical information, such as your headlines or the content itself are actually images.
As discussed earlier, this is a huge issue as Google cannot accurately process this information and is currently not using it to rank websites.
Ensure any and all content that can be expressed in words, are actually present as words.
Set Up an Image Sitemap
A sitemap is an overview of all of the content on your site, generally used to index articles. Well, you can also create an image sitemap which tells Google about all of the media files on your site.
This can help index new pages and images faster and ensure nothing gets missed (e.g. images that are loaded via javascript).
Here’s the WordPress plugin we recommend for image sitemaps.
Image SEO FAQ
We update this post once a month with any changes to the main content and also add additional questions from both our clients and readers.
Here’s what others have asked:
How Many Images Should I Have on Each Page?
Just like with word counts, keyword densities, or anchor text ratios – there’s no one magical answer in 2019.
Your best bet is going to be reverse-engineering the top five results for your main keyword.
Pull up articles that are already ranking and take a look at how many images they are using in their content.
While this isn’t a super scientific approach, it may show that for some topics, Google prefers image-rich or video-rich content.
At the same time, if you feel like a post would be more valuable with additional images or media, don’t be afraid to deviate from this number.
Use it as a guideline.
Does Image Metadata Affect SEO?
All image files contain metadata (EXIF and IPTC) that stores information about how the photo was taken (camera, focal length, etc) as well as things like the date it was taken, the location, and copyrights.
Google’s statement on this has been that it may or may not be a ranking factor but they reserve the right to use it. ¯\_(ツ)_/¯
Lucky for you, most image compressors (discussed above) strip this data for you and this is the way I prefer to go for the majority of businesses.
But I also reckon there’s a small chance that if you’re trying to rank for local terms (such as Charlotte SEO company) you may benefit from having real photos taken in the area that contains the metadata.
On Page SEO Guide – The 80/20 Of optimizing your site for on-page seo
The theory behind on-page SEO is simple: make your site easier for search engines to understand and rank.
This can be taken literally: don’t block search engine spiders from your site; and a bit more philosophically: create a site that search engines want to rank highly and serve to their users.
The number one problem I see with sites trying to rank in Google for even medium-difficulty keywords is content. Google doesn’t want to serve your super thin, short, repurposed content site to its users.
The reason they’ve become the biggest search engine (by far) is that they have been capable of providing the best, most relevant results for users problems.
As we’ve shown before, in previous on-page related posts, just improving and optimizing your existing pages can create massive improvements.

Use this guide to crush your site’s on-page SEO and watch the rankings improve (especially if you’re using our services).
Content
Create Unique content on all pages
You must write unique content for your site. Stop stealing other people’s content. Google does not rank stolen/scraped content unless your site is CNN or Amazon.
You need unique content on all of your pages. A Panda Penalty can be tripped if even 30% of the pages on your site are low quality (FYI, panda is a site-wide penalty, so you can kill your entire site–or never even rank in the first place if you get a penalty like this.)
It’s like your grandma always said…

Write Longer Content
The days of ranking for keywords with 500-word articles are long go. In fact, these will likely do more harm than good.
In the last few years, SEOs have started to notice that longer content ranks better. This has led to people pushing it further and further, with some guides going over 10,000 words.
However, the truth is that longer content isn’t always better.
Instead of just pushing out “2,000 word articles” like everyone in the industry is preaching, take a look at what is already working.
Google the keyword you’re attempting to rank for and look at the length of content (and format!) of the top five articles.
If each of them are around 1,350 words and in the form of a listicle – go for a 1,500 word listicle.
When all you’re presented with is 5,000 word behemoths with videos and images, you’ll want to do the same thing.
Check out our full-guide on creating content that ranks.
Utilize Related Keywords
Use industry related keywords within your content: if you’re trying to rank for “Apple computers,” then be sure to include related keywords in your content (Steve Jobs, iMac, iOS, better than a PC, etc)
Here are some ways to find related keywords:
Google Autosuggest:
If you navigate to Google.com and start typing in your main keyword (in this case, “Apple“) Google will supply a short list of related words:

Searches Related To
Once you actually perform the search scroll down to the bottom of the page for some related searches:

Answer The Public
Answer The Public does all of the work for you by automagically mining Google’s auto-suggest results for additional ideas.
It takes common question words, along with your keyword, and then looks at what Google suggests:

Not only that, it will do the same with common prepositions, comparisons, related searches, and every single letter from the alphabet.

Pretty cool, huh?
Premium – See What Competitors Rank For
This is my absolute favorite SEO strategy.
There’s a catch though, you need a paid piece of software called Ahrefs. It can do a million and one useful things when it comes to SEO.
For now, we’re going to use it to see which keywords our competitors’ article ranks for, so we can ensure to target the same, proven keywords with our own content piece.
You simply plug in the URL of the competing page and click on “Organic Keywords” in the sidebar.

We can quickly see that our competitors’ on-page SEO guide is ranking well for terms like “on page SEO checklist” and “on-page SEO techniques” so it’d be wise for us to include those in our piece.
Need more help with this? We’ve got a massive guide on keyword research that’ll cover every strategy we use at Smash Digital and the exact processes and logic behind them.
Stop Keyword Stuffing
You do not need to mention your target keyword over and over again.
You can, and will, get penalized for doing this. Use your keyword naturally a few times within your content, that’s it!
Again, if you’d like a guideline for this, reverse engineer what is specifically happening for this keyword in the search result.
How many words of content does the number one page for this result have on their site and how many times do they use various keywords?
You don’t have to reinvent the wheel when you can see exactly what is working.
Build a Big Site
You need a healthy-size site. Your website should have at least 20 pages of quality content. This is the bare minimum.
The more the merrier applies as long as you are able to maintain high-quality content.
If your site is only 1-5 pages, you will have an uphill battle trying to rank, and when you DO rank, getting any results will take 3x as long.
Create Engaging Content
Making a big site of boring stuff is not the answer.
Google is smarter than you. It can tell if the content you are writing is engaging or not. In fact, it tests your site anytime anyone visits it. It’s testing the user metrics (and that is not only time on site).
If you are not creating good, quality, engaging content, your users will peace out and Google will never rank your site.
In fact, I would say you could ignore half of this guide if you would only create hyper-engaging super ninja awesome content that people would love.
If you get people to engage, you will always win.
Theme and Intent of your Content
When you’re looking to rank for a certain term, I recommend Googling the keyword. Look at the type of content that is currently ranking.
It should be very easy to see if Google is treating it as an informational query or a buying query (commercial).
Tailor your content to match what Google shows.
If Google treats it as an informational query (the results aren’t trying to sell you anything), then you will have a hard time trying to rank a site that doesn’t fit in with that intent.
The opposite is true as well. If Google is only showing you product pages and e-commerce stores, you’re not going to rank your 5,000 word article about “the best wireless headphones”.
Example of an Informational Query:

Here’s an example of an informational query, where Google is ranking pages that convey information. You’d have a hard time ranking a page that was explicitly trying to sell something for this keyword:
Example of a Buying Query:

Here’s an example of a buying query, where Google is ranking pages that are pushing products. You can more easily rank a page trying to sell something for this query, and, as you can see, you’d have a better chance of ranking a page trying to sell something than not:
Meta Data
Meta data serves two important functions:
1) It helps to tell the search engines what your site is about
2) When your site shows up in the SERPs, it helps convince people to click on your site instead of your competitors

Meta Title Optimization
The meta title should sum up what your page is about. You could also try to add in a unique selling proposition to stand out and attracts more clicks thank your competitors.
Example: Apple Computers – Buy Them Here
It’s short, simple, and to the point.
Meta Description Optimization
The meta description gives more details as to what your page is about. Use this text to convince people to click on your site instead of your competitors.
A high click-through rate will increase and solidify your rankings. Make it sexy!
Examples: Save up to 45% on all Apple products. All iPhones, iPads, and Mac computers on sale. Free shipping limited time!
See how you are giving the searcher an incentive to click on your site? That’s what you want.
You can use your main keyword in the meta description or not. I personally like to use variations of the main keyword combined with buying keywords.
Here’s an example with some meta descriptions:

How to Edit Meta Data on WordPress
You can easily start customizing the meta title and meta description if you’re using WordPress by installing one of these two plugins:
All in One SEO – use this if you’re an SEO rookie.
Here’s how to install and setup All in One SEO Pack:
https://www.youtube.com/embed/gwB8cVgrbW0
Yoast WordPress SEO – use this if you’ve got a decent understanding of SEO
Here’s how to set up the Yoast WordPress SEO plugin (produced by the Yoast.com team):
https://www.youtube.com/embed/i3E_dkxib4M
Heading Tags
Headings on your website shouldn’t just be bold. There are specific HTML tags to indicate the importance of different titles and headings. These are a ranking factor for search engines:
- <H1>Very Important Title</H1>
- <H2>Important Title</H2>
- <H3>Less Important Title</H3>
These go down all the way to H6.
How to Structure Your Posts Using Heading Tags
You want to treat each piece of content you are creating as if it was a book, separated into chapters and subchapters.
This helps you keep longer posts skimmable and also give readers a heads up of what’s coming in the next chapter.
Also, when a longer, more comprehensive guide is ranking for hundreds of different keywords, headings are a great way to rank for additional keywords as well as featured snippets.
Keep your headings descriptive, keyword rich, and compelling to the user.
Note: You should only have one H1 tag per page and depending on the content management system (CMS) you are using (e.g. WordPress) this may already be the title of your article.

Example of a Page with Optimized Heading Tags
To give you an example of how we optimize headings, take a look at the table of contents for our image optimization guide.

URL Structure
Whenever possible, keep your permalinks short and simple, preferably with a main keyword in it as long as it’s not spammy looking.
Permalink Example
Let’s use our own site as an example.
“Fully managed SEO services” is not only easier for users to understand and remember, but also give search engines an idea of what the page is about.
A bad example would be something like “smash.digital/what-we-do/”
Ranking Homepages vs. Inner pages
Do a search for your main keyword and make note of the type of pages Google is ranking. Are the majority of the pages homepages or inner pages? If the top 10 is currently full of inner page blog posts from sites, and you’re trying to rank your homepage, you’ll have a much more difficult time making it work.
Here’s an example of a search query where the majority of the results are the homepage. In this situation, you should try ranking your homepage for this keyword if you were targeting “carpet cleaning service”

Here’s an example of a search query where the majority of the results for the search “woodworking tools” are inner pages:

Media Files
This refers mainly to the images and videos found on any given page of your website. You definitely want images and videos to be present. It absolutely helps with ranking sites.
Videos
Using videos for SEO is simple: embed a relevant YouTube video. This is one of the best things you can do to improve relevancy of a page AND improve on-page metrics like time on page!
Simply search for something relevant on YouTube (e.g. “apple iMac review”) and click “Share” below the video.

Next up, click on “Embed” and simply copy the code that it gives you. It should start with “<iframe…”
In the WordPress post editor, click “text” then paste it in:

Easy!
Image Optimization
We’ve just published a 2,000+ word image optimization guide you should check out. It covers both the SEO side as well as speed optimizations.
But here are some of the key principles…
File Name
Google cannot understand images the way we do, but they can read text…
Change the file name to something descriptive before uploading your image to WordPress.
Example: Refurbished-Apple-iMac-2019.jpg is better than IMG-4322.jpg
Alt Tags
Use an “alt tag” for each image that you upload. This is another easy way to tell Google what this image is about and show them that it is relevant to the page.
You’ll want to write something that includes a keyword that people might search for, but also describes the image.
In WordPress, you can edit alt tags when you upload an image to a post:

For example, the alt text on the image above could be “how to add alt text to images on WordPress”.
Image Over Optimization
The majority of people who read about image optimization start to massively over-do it and risk getting penalized.
No, you don’t want to call all 21 images on your blog post “apple computers” and “apple computers reviews”.
Sure, it’s great if you can include a keyword in the file name and alt tag, but they should be related to the image and the text around it, not your main keyword for the page.
Image Size and Speed Optimizations
You want to “compress” the image file size before posting. This will make your site load faster.
If you have a Mac, you can use a piece of free software called ImageOptim.
For the Windows folks, you can use the online version of ShortPixel.
This is a super easy way to make image file sizes up to 90% smaller and skyrocket your site speed.
Which leads us to…
Site Speed Optimization
Fast sites rank better.
More importantly, your potential customers won’t wait for a slow site to load and will hit the back button instead.
These are two of the reasons why I suggested compressing your images. Huge images take a lot more time to load than smaller or compressed (size) ones.
Site Speed Testing Tools
The two tools we use the most to test site speed are Pingdom and GTMetrix.
Both are great and give you different insights into why your site is loading at the speed it is.
How Fast Should My Website Be?
Make sure your site is at least in the 80th percentile for load time and loads under two seconds. Having a site in the 90th-100th percentile and a sub-one second load time is definitely better, but I personally don’t see evidence of needing to be higher in the 80s to get the benefit.
If your site is coming back as SLOW, follow the advice that Pingdom and GTmetrix give you.
If you’re using WordPress there are some very simple steps you can take to speed up your WordPress site with just a few minutes of work.
W3 Cache Plugin
Install the W3 Cache Plugin and activate it (unless you’re using WPEngine as your host).
In the WP dashboard, go to Performance > General Settings

Enable “Page Cache” and “Minify” and then save the settings.

Now, check to make sure your site is working properly.
“Minify” can sometimes mess up a site. If it did mess it up, deactivate it and the problem should be solved instantly.
After you’re done, check your page speed again to see how much it has improved.
Lazy Load Plugin
If your site is displaying a lot of images, try the “lazy load” plugin.
It delays the loading of an image until the visitor scrolls to that part of the page. So, if your article uses 10 images in a long post, it will only load the first few images, and will load each image after that as the visitor scrolls down.
Here’s the link: Lazy Load.
Plugin Relation to Site Speed
Keep an eye on your plugins. If you’re not using a plugin, deactivate AND delete it. Plugins, even deactivated ones, can slow your site WAY down.
You can also see from Pingdom and GTMetrix if a specific plugin is slowing your site down significantly. If this is the case, it may make sense to find a faster alternative.
Cloudflare
Feeling adventurous?
If you’re comfortable using WordPress and are a bit more tech-savvy than a beginner, check out Cloudflare – a content delivery network (CDN).
It distributes your content to multiple servers around the world, delivering your site faster to your visitors.
It’s really not complicated, and I recommend that you use it. It’ll take you about five minutes to set up.
If you’re a media-rich site, it can cut your load time in half.
Half!
Here’s a quick tutorial if you want to give it a try:
https://www.youtube.com/embed/-FWhBwEeDls
Fastest Website Hosting Companies
If you’re using WordPress, then I cannot recommend enough that you use WPEngine.
It’s an all-in-one WordPress managed hosting solution. In my experience, it’s the easiest way to speed up your site instantly! It has a built-in CDN and is completely managed for you (updates are automatically downloaded and installed).
Another highly recommended managed WordPress host is Traffic Planet Hosting. It offers the same quickly-loading site as WP Engine (probably faster actually), but is much cheaper.
I will say that if I wasn’t already on WPEngine that I would go with Traffic Planet.
Want more? Surprise, surprise – we’ve got a full guide on optimizing site speed ready for ya.
Schema Markup (for Local Sites)
If you’re targeting a specific location, you need to use a “schema markup” to give the search engines information about what you are and what locations are relevant to your business.
Schema is an accepted form of structuring data that our search engine friends can use to understand your site.
Schema markup is very easy to add. If you’re like most local businesses, you have your name/address/phone number/website (NAPW) in your footer. Just replace it with the following code.
<div itemscope itemtype=”http://schema.org/LocalBusiness”>
<h1><span itemprop=”name”>Your Biz Name</span></h1>
<span itemprop=”description”> Service description with some keywords sprinkled in.</span>
<div itemprop=”address” itemscope itemtype=”http://schema.org/PostalAddress”>
<span itemprop=”streetAddress”>Your Address</span>
<span itemprop=”addressLocality”>Locality/City</span>,
<span itemprop=”addressRegion”>Region</span>
</div>
Phone: <span itemprop=”telephone”>523-355-3222</span>
</div>
Replace all the info with relevant info to your own business in the above example
There are actually countless things that you can markup if you’re feeling adventurous (videos, images, etc), but the above code for local sites is a must.
Testing Schema Markup
Once you’ve added the markup, test it to make sure it is implemented properly by visiting http://www.google.com/webmasters/tools/richsnippets
Crawl Your Site Using Screaming Frog
Finally, check your site for major errors by running a search using the Screaming Frog SEO Spider tool. It’s free, and an awesome, powerful tool.
There’s TONS of things you can look for, but the most important will be making sure the status codes say either “200” or “301.” If you see anything else, then you or someone you know more knowledgeable should take a look at getting those fixed. They can cause really big problems.
So, this concludes the 80/20 of On-page SEO.
Kinda simple huh?
I should probably put some sort of catchy ending and a call to action, but instead…

How to Find Long Tail Keywords With NO SEO Competition
This article was originally published as a part of the mddigitalgraphicdesigns Inner Circle.
It’s the private newsletter for our clients, partners, and friends, where we share one super actionable SEO tip that has worked well for us, every week.
If you’d like to get these months before the public, you now have the chance to do so by filling out the form below.
Let’s get straight into it…
Our Go-To Strategy For Finding Easy Keywords to Target
We’re going to kick things off with one of my favorite strategies for finding super low competition topics that bring in tons of organic traffic.
I can already hear you saying “this cannot work for my industry because of X, Y, and Z”.
It can and it will.
In fact, we use this strategy ourselves to find topic ideas in one of the most competitive niches out there – SEO.
Is the suspense killing you yet? Let’s dig in.
Time to learn: 5 minutes
Impact (1-10): 7
Tools required: Ahrefs
If you’ve spent any time at all in the SEO world, you’ll know that backlinks are by far the most important thing when it comes to increasing your traffic.
You could have the greatest content in the world, perfect on-page SEO, and a bunch of social media activity but if your site doesn’t have any links to it, it’s not going to get much traffic.
Unless…
Once a website has a significant amount of links pointing to it as a whole, Google will start to trust it more and more.
This is what we call being an “authority”.
These authority sites will often be able to rank for low competition keywords without having to do any link building or sometimes even proper on-page SEO.
Awful, isn’t it? All these big brands stealing all of our traffic…
Not quite!
In most cases, this is a great opportunity for us to jump in with a highly-optimized page, with better content, and some backlinks to the page.
How to Find These “Unicorn” Keywords
As mentioned in the introduction, you’re going to need a tool called Ahrefs for this.
They’re the second most active web crawler in the world, after Google, and their only objective is to give SEOs and marketers data.
We’re going to use their computing power to our advantage.
You’ll want to head over to their Content Explorer and type in a keyword related to your site.
In this case, we’re working on an eCommerce site that sells outdoors equipment such as tents, hiking boots, and other gear.
I’m going to type in hiking as the keyword and then apply the following filters:

- Change search “Everywhere” to “In title” next to your keyword
- Set the language filter to “English
- Add a new filter for “Organic Traffic” for a minimum of 400
- Add a new filter for “Referring Domains” at 0
What comes up is a list of 32 different articles that are really low competition but getting a great amount of traffic.
Here are just a few topic ideas I covered that may be a fit for our eCommerce store and what keywords they rank for.
1. Hiking in Iceland | Iceland’s Best Hiking Routes
- Hiking in Iceland
- Best hikes in Iceland
Estimated traffic: 457
2. The Best Hiking Trails Near Sacramento, CA
- Hiking near Sacramento
- Best hikes near Sacramento
- Hiking trails near Sacramento
Estimated traffic: 860
3. Every Hiking Spot Near Cleveland You Need To Explore
- Hiking in Cleveland
- Best hiking in northeast Ohio
‘Cleveland hiking trails
Estimated traffic: 2,300
“Yeah but none of these keywords is going to get me any sales!!!!!”
That’s a whole other debate but here are some points to consider:
- Some will convert
- Ahrefs generally underestimates traffic by a third
- These pages will stay live and rank for months or years (it compounds)
- Most of these topics are 600 words and don’t take much time
But to counter your argument…
4. Best Hiking Pants for Women (Plus 8 Hiking Leggings)
I’m sorry but this one just screams money…
- Hiking leggings
- Hiking tights
- Best hiking pants for women
- Waterproof leggings
- Best hiking pants
- Best hiking leggings
More? Sure thing.
5. The 10 Best Hiking Sandals in 2019
- Best hiking sandals
- Closed-toe hiking sandals
- Best hiking sandals for men
- Best hiking sandals for women
Estimated traffic: 465
I’m going to stop now but here are a few more results I found just by typing in ONE keyword and going through ONE page of results (along with the ones mentioned before):
- The Best Hiking Shorts for Women of 2019
- The Best Waterproof Women’s Hiking Pants
- 10 best men’s waterproof trousers for walking and hiking
- The Best Hiking Shorts for Men of 2019
- This Hiking-Inspired Modular Backpack from Japan Sold out Instantly
Now go out there and start experimenting with different keywords and see what you can dig up.
Next time, I’m going to show you how to analyze your competitors’ articles to create an outline for an article that’s going to rank well in Google.
8 SEO Strategies to Get Google to Trust Your Site
This article was originally published as a part of the mddigitalgraphicdesigns Inner Circle.
It’s the private newsletter for our clients, partners, and friends, where we share one super actionable SEO tip that has worked well for us, every week.
If you’d like to get these months before the public, you now have the chance to do so by filling out the form below.
Does Google TRUST You?
This probably doesn’t come as a surprise but Google owns more than 20,000 patents and they’re registering around 10 new ones every day.
Among them, we have this patent from 2006 for “search result ranking based on trust”

What a shocker! To decide whether you should be ranking or not, they are looking at whether your site is trustworthy.
Today we’re going to look at some of the factors they are likely putting into consideration when making this decision.
Time to learn: 5-10 minutes
Impact (1-10): 9
Tools required: None
What Are Trust Signals?
For anyone who has ever put up more than one website, you’ll likely notice that you put different amounts of effort into them, depending on how seriously you took the project.
When we start our more important businesses, such as Smash Digital, some of the first things we did were to ensure we own all of the social media handles, have a registered entity, and register with Google My Business.
Do we do the same when starting a new affiliate website or side project? Hell no, it takes too much time.
Now if you were Google… A technology company specializing in algorithms and analyzing over a billion pages – do you reckon you could see a pattern with this?
Now, I’m no mathematician but I’m going to say this is fairly easy for them to do.
Even for ourselves, just by looking at a website for less than five seconds, we can get a pretty accurate gauge of whether they’re legit or not.
So what can we do to prove to Google that we’re legit?
8 Easy Ways to Increase Your Trust With Google
This is going to sound obvious but to sum up this whole topic – you need to act like a real business and show that to Google.
Here are some suggestions on things that may help you with this and fuel some additional ideas – in no particular order:
1. Social Media Presence

Social media is dominating the modern world. I see entrepreneurs registering their businesses social handles before even figuring out what they’re going to sell, buying a domain, or setting up a website.
This is one of the biggest red flags in my head.
I challenge you to find some truly successful companies that don’t have any kind of social presence.
This doesn’t mean that you need to focus on getting a million followers or churning out content like a madman.
Simply register them, link them to your website, fill out the profiles properly, and share something every now and then.
2. Google My Business

If your goal is to get visitors from Google, does it sound like it may be a good idea to create… a business profile with Google?
For most real businesses, especially local ones, this is one of the first things they do when getting their website up.
A super easy way to instantly get more search visibility, give Google information about what your business does, and show that you’re serious about this.
As always, the more information you can provide on your profile, the better.
It doesn’t take long, put in the work.
3. Business Citations

While business directories and citations have become slightly less popular with the growth of social media, they still matter.
Get your business set up on any relevant business directories, both for your niche and locally.
This might include things like:
- Yellowpages
- Yelp
- TripAdvisor
- Apple Maps
- FourSquare
- Capterra (software specific)
- Clutch.co (agencies)
- Angel.co (tech)
The same tip applies as for Google My Business – take the profiles seriously and fill them out with unique information.
Not only do these count as a trust signal and help grow your backlink profile, they provide:
4. NAP and Consistency
NAP stands for name, address, phone number – the essentials of what you’d expect from a business you’re giving money to. A massive signal of trust.
You need to have these present on your website and you also want to use them on your various profiles – social, citations, Google My Business, etc.
The other important thing is to keep them consistent. Always ensure your address is written in the same exact way, the phone number follows the same format, etc.
This is especially crucial for local businesses.
5. Brand Mentions
While backlinks (links from other websites pointing to yours) are the main ranking factor in Google, they are not stupid.
Unlinked mentions of your company and brand are just as important and often serve as justification for other ranking signals you may have acquired, such as links.
Is it not weird that 300 websites have linked to your website with the words “buy laptops online” but the name of your company has never been mentioned on the internet?
To me, that’s quite a clear signal of some sort of manipulation.
I’m betting Google will agree with me here.
6. HTTPS

While having a secure website is a ranking factor in itself, I think it ties in pretty well with trust as well.
Real companies value the security and safety of their customers and that’s what using HTTPS gives you.
Hell, Google Chrome even gives you a massive red warning when trying to access un-secure websites now – it’s clear Google cares about this.
7. Terms of Service/Privacy Policy
Yet again, I encourage you to try and find a legitimate business that does not follow privacy law.
You need to have these key trust pages on your website:
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
- Any necessary disclaimers (e.g. affiliate)
- A contact page
8. Who Do You Link To?
Legitimate businesses are there to help their visitors find solutions to their problems, not just promote their own products.
If the only sources of information on your website are your own articles – it’s a red flag.
Real authorities have references to various case studies, statistics, or research.
You should be doing the same.
Wrapping Up
This is not a definitive list but it should be enough to get Google to trust you to a large extent and perhaps even inspire additional ideas.
What else do you think Google looks at to figure out if you’re trustworthy? Send us your theories – whether proven or wild! 🙂
That’s all from me for this week.
I’ll see you next week with yet another actionable SEO strategy.
Site Speed Optimization 101 – An Easy Blueprint to Increase SEO Traffic and Leads
This article was originally published as a part of the mddigitalgraphicdesigns Inner Circle.
It’s the private newsletter for our clients, partners, and friends, where we share one super actionable SEO tip that has worked well for us, every week.
If you’d like to get these months before the public, you now have the chance to do so by filling out the form.
The Greatest SEO Hack Since… Ever?
There is an amazing SEO hack that has been spread around massively in the last couple of months and today we’re going to show you exactly how to implement it for your own business.
What makes this strategy so special compared to everything shared in the SEO world?
- It is practically instant
- It doubles the real-estate you take up in the search results
- Increases your branding
- It actually helps your readers!
Let’s get straight to it.
Time to learn: 5-10 minutes
Impact (1-10): 8
Tools required: Rich Snippet Generator (it’s free)
Introducing FAQ Schema
Take a look at this search result.
See anything different from your average Google search?

DreamGrow takes up nearly half of the page with their frequently asked questions.
Today I’m going to show you, real-time, how to implement this on your own site in under five minutes.
Want to know the best part about this?
YOU decide what the questions are and what you write in the answer box and Google displays them near instantly.
As they say… With great power comes great search traffic – or something along those lines…
Before you proceed with this, I highly encourage you to check out Google’s guidelines on using the FAQ schema and don’t abuse it. This way we can all reap (moderate) benefits from this for years to come.
If the page doesn’t have any relevant questions to be covered, don’t use the schema.
Another no-go solution would be implementing it on one of your product pages and only using questions to hype up your own stuff.
Use common sense and ask yourself – would Google users actually benefit from this?
Getting Started – Coming Up With The Questions
First of all, you’re going to need a list of frequently asked questions to use.
There are a few ways you can go about this, but here are my favorite strategies:
1. Look at the “People Also Ask” section
Naturally, being in the SEO game, my first choice for questions is going to be what Google already thinks is relevant for my queries.
Let’s say I had a post about the best protein powders, here’s what Google shows me that “People Also Ask”:

Not only does Google think these are relevant, but I could also see these being quite helpful for our content.
2. Use Answer The Public
Answer The Public is a handy tool that finds every question possible related to your keyword.
Here’s just a glimpse into what it gives us when we type in “link building”:

Now just use your head to figure out what’d be the best fit for your users.
3. Come Up With Them Yourself
If you’re the one creating the content, it’ll probably be really easy to come up with the questions on your own and just make it a part of the article itself.
For example, if I’m writing an article about link building, I would already know that most people will ask me about how many links to build, what types to use, and whether buying them is OK.
But still… I like to draw inspiration from what Google gives us on a silver platter with the People Also Ask feature 🙂
Tips For Writing The Answers
While you can write whatever you want as the answer, I’ve got two main tips for this:
1. Actually answer the question and be useful
Quite self-explanatory, huh?
2. Create curiosity and encourage people to read the article
If you look back at the FAQ example given above, it is generally going to be plain text which means there is no way to click to the actual page.
Since our goal is to get people on the site, answer the question to some extent but hint that there are more details in the article itself.
Here’s an example of how I might do it for: “What’s the best link building strategy?”
“There are dozens of link building strategies outlined in this post and they all work, but ultimately, the best strategy is going vary for every industry. What works well in sports, may not work in digital marketing. Overall, we’ve had the best success rate with strategy #4.”
We start off by mentioning that our actual post has a list of strategies they can use and finish off by recommending a specific strategy they can only learn by reading the article.
Curious? I would be!
Another, slightly shadier strategy you can use here is to pretend the results are getting cut off.
Something along the lines of:
“In our case study of building 5,325 links using 7 of the most popular link building strategies, there was a clear winner. Assuming you follow best practices, the most effective link building strategy is…”
Now, we don’t recommend the second approach but it might just get your creative juices flowing 🙂
How to Actually Implement The Results
As a recurring theme in these inner circle emails, there’s a bunch of ways you can implement this…
There’s a slightly harder way, by following the Schema markup provided by Google on their guidelines page.
And then there’s the easy way…
SEO blogger Matthew Woodward has been kind of to create a free FAQ rich snippet generator on his site that’ll automagically make the code for you.

Simply fill in your questions and answers and it’ll give you a piece of code to put into the header of the page you’re trying to get a snippet for.
I like to use the Insert Headers and Footers WordPress plugin for this as I already had it installed on my site.
If you’re using Matt’s tool, he also lists a bunch of other ways to implement the code, so check that out.
Let’s See It In Action
Now, I promised you that this would work in less than five minutes so let’s see how it works.
First, here’s a screenshot of the results for “Dropship Lifestyle Review” at 2:46 PM.

To be fair, I did write up the questions and answers before that, but it’s fast none-the-less.
Next up, I went into WordPress, edited the post to actually have the FAQ text on the page itself, and added the code to the header of the page.

Now we need to let Google know that the page has been updated and ask them to recrawl it.
To do this, you can head to Google Search Console, navigate to “Coverage” and then look for pages that are “Submitted and indexed”.

Now on the bottom of the page, you’ll find a list of all of your indexed posts.
Find the one you just updated, click on it the result, and choose “Inspect URL” from the right-hand sidebar.

As the last step, on that final page, you’ll see a button for “Request Indexing” which tells Google that the page has been updated and puts it on their priority list.
Now we wait for Google to go over it…
And voila, just 5 minutes later, the search results look like this:

Try it out and report back on how it goes – we’re looking forward to your success stories!
Let me know if you have any questions and I’ll see you next week with yet another actionable SEO strategy.
How to Build Guest Post Links (The Right Way) for SEO Dominance
This article was originally published as a part of the mddigitalgraphicdesigns Inner Circle.
It’s the private newsletter for our clients, partners, and friends, where we share one super actionable SEO tip that has worked well for us, every week.
If you’d like to get these months before the public, you now have the chance to do so by filling out the form below.
Our Go-To Link Building Strategy
The number one link building strategy we use for Smash Digital, our portfolio of businesses, our investments, and of course, our clients – is guest posting.
But there’s a major flaw with the way most people are taught how to do it.
Today, we’re going to show you how to do it right.
Time to learn: 5-10 minutes
Impact (1-10): 10
Tools required: None
Tools suggested: ahrefs
Now, let’s get to it…
What’s Wrong With Guest Posting Tutorials?
If you’ve ever tried to do guest posting on your own, you’ve probably seen these tutorials already.
They go something along the lines of:
- List down some keywords related to your industry
- Combine them with search parameters such as:
- “Write for us”
- “Submit a guest post”
- “Guest post guidelines”
- Etc
- Pull all the results together
- Add SEO metrics (domain rating, number of links, etc)
- Find the owners email or the guest posting page
- Start pitching
While this is an acceptable approach, it’s got two glaring issues with it.
First of all, this is the way every newbie SEO has been taught to do guest posts. In fact, they probably all send the same email templates as well.
Not only that, spammers have been automating these queries for close to a decade now which means…
This is the best way to find guest posts… that have been spammed to death and have no quality standards.
There, I said it.
Sure, you can find some acceptable sites using this way and get some results.
But there’s a better way.
How We Find High-Quality Guest Post Opportunities
If you’ve read any of our other actionable SEO tips, you can already guess which tool we’re going to use to make this happen.
Let’s open up Ahrefs’ Content Explorer and we’re effectively going to use the same approach as the previously mentioned guides do.
You’ll want to type in phrases related to your industry.
I’m going to use email marketing as an example, so I might type in something like “email subject line”.
That presents us with every single article Ahrefs has ever crawled related to email subject lines, which is about 63,000 pages.
Since we’re going to be guest posting on websites, not pages, we’ll want to add some filters:
- Show one page per domain
- Only show English results
- Pages that are live
- Minimum domain rating of 30

This narrows it down “just” to around 10,000 guest posting opportunities for us.
You’re probably wondering why we’re assuming these websites accept guest posts in the first place?
The truth is that we never do but all it takes to find out is to send them an email. Any type of outreach-based link building is generally a numbers game, but a good pitch goes a long way (more on that shortly).
While this means it might take a few extra emails until someone accepts your pitch, these sites are also going to be much higher quality.
P.S. You can technically apply the exact same strategy without Ahrefs but it’ll be a lot of work.
Additional Guest Posting Tips
Different strokes for different folks…
If you already have a super authoritative website (let’s say DR65+) with tons of links, you’ll want to focus your efforts on getting higher authority links.
This means you’ll also have to create much higher quality guest articles and put more effort into your outreach emails. Higher authority sites tend to have higher standards and can be harder to reach.
For those of you with a newer website or simply a weak backlink profile, even an “average” link can go a long way in improving your results.
In this case, you might want to set an additional domain rating filter – to only show sites between say DR25 and DR50. They will be less strict with the content required and easier to reach. You’ll be able to attract a whole lot more links as you build up your authority.
That’s all from me for this week.
Next week, I’m going to show you how to write the perfect guest post pitch.
Let me know if you have any questions and I’ll see you next week with yet another actionable SEO strategy.
Anchor Text Optimization – Everything You Need to Know
This article was originally published as a part of the mddigitalgraphicdesigns Inner Circle.
It’s the private newsletter for our clients, partners, and friends, where we share one super actionable SEO tip that has worked well for us, every week.
If you’d like to get these months before the public, you now have the chance to do so by filling out the form below.
WTF is Anchor Text?
If you’ve done any link building to grow your business, you’ve undoubtedly heard of anchor text.
Anchor text is the clickable part of a link (the bit that is usually blue in color and underlined) and it has been a part of Google’s search algorithm since the very beginning.
Why? Because anchor text is an outside signal to Google that may indicate what a specific page is about.
When 6 different websites link to a page with the anchor text “SEO guide” – it’s quite likely that that page is, in fact, about how to do SEO.
Does that mean you should be smashing all of your links with the keyword you’d like to rank for?
That’s what we’re going to talk about today…
Time to learn: 5-10 minutes
Impact (1-10): 8
Tools required: None
Tools suggested: None
Now, let’s get to it…
A Bit of Background on Anchor Text
As mentioned earlier, anchor text has historically been a major way for Google to understand what a page is about and was a major contributor to their success as a search engine in the early days.
Unsurprisingly, SEOs were quick to start manipulating this and things went a bit sideways.
Back in the day, you could even rank pages for keywords that didn’t exist on the page itself by using targeted anchor text – click here to read about Google bombing for some extreme (and hilarious) examples.
You may have heard of the Google Penguin update that first got rolled out in 2012 – anchor text manipulation was one of the main things they targeted with that and a lot of websites got penalized because of it.
Ever since then, they’ve gotten more and more strict with anchor text usage and the risk of getting your site slapped is real.
Before we dive into the actual usage of anchor texts…
Types of Anchor Text
Because you can set whatever you’d like as the anchor text, categorizing them makes it a lot easier to process the data around them.
Generally we divide them into six primary categories.
Let’s pretend we’re trying to rank SmashDigital.com for the keyword “SEO agency” and use that as an example.
Exact Match – This would mean linking to our website with the anchor text SEO agency.
Partial match – Contains the keywords but not in the exact order.
“For growing search traffic, we recommend working with an SEO expert or agency.”
Phrase match – Contains the exact keyword but also additional phrases.
“mddigitalgraphicdesigns is an SEO agency run by unicorns.”
Branded – When you link back with the brand name or a variation of it.
“We’ve heard mddigitalgraphicdesigns has an awesome newsletter, you should check it out!”
URL – A link back with the URL or a variation of it.
“Want to learn more about our link building services? Have a look here: https://mddigitalgraphicdesigns.net/ link-building-service”
Misc – This includes everything generic that doesn’t include the keyword itself. Common examples are:
- Click here
- Check out the case studies
- This case study
- Travis Jamison’s company
- On their website
Optimizing Your Anchor Text
If you’re taking SEO seriously, you’re most likely actively building links and not waiting for them to magically appear. This means you’ll also have control over the anchor text (e.g. in a guest post).
Because exact match anchor text used to be super effective, a lot of SEOs are still using them quite aggressively – but is this the right play?
I’m confident in saying that about half of the websites we’ve seen with Google penalties in recent years have overly aggressive anchor text to blame for it.
On the other hand, while some case studies show that there is no correlation between using exact match anchor text and higher rankings – our experience shows that they still work.
So what should you be doing?
A lot of SEO experts will recommend you to optimize it on a case-by-case basis.
This means that if we wanted to rank for “SEO agency”, we’d have to Google the keyword, analyze the anchor texts of the top ranking pages, categorize them and calculate the percentages of each group and try to replicate that.
While this sounds great in theory and makes for a great article… The reality is that there is going to be so much variance from site to site and more often than not you won’t even have enough data.
We’ve tried doing this in the past and saw no difference in results.
Our general approach is on the safer side and we like to diversify it as much as possible, especially throughout the site.
This is often a 40-60% split between keyword-oriented and generic anchor texts.
On the keyword side we would use one or two exact match anchors at most and balance the rest between longer (3-6 words) phrase and partial match keywords. Add in some long-tail/related keywords to the mix and you’ll be good.
The other half is going to be generic texts and this is where you can get creative and try to make it look as natural as possible.
Some examples:
- Call-to-actions
- Read this guide
- Check out the study
- Find out more here
- Compare the pricing
- In this post
- Branded and alike
- Smash Digital
- SmashDigital
- Smash agency
- A study by Smash Digital
- Travis Jamison’s company
- Article by Travis Jamison
- Travis has written
- Thematic
- 91% of successful companies do link building
- By having an optimized website
- Building better quality links
- Can improve organic rankings
- Links with a relevant anchor text
- URLs
- https://mddigitalgraphicdesigns.net/fully-managed-seo-services
- mddigitalgraphicdesigns.net/fully-managed-seo-services
When in doubt, just use existing words in an article instead of trying to stuff your link in.
You can also use a tool such as Ahrefs to draw ideas from your competitors’ links (hey, look at how natural that anchor text is!)
It really doesn’t need to be more complicated than that.
I’d say the main advice we have for this is to diversify as much as possible and try to stay contextual and natural.
Surrounding Content
Lastly, keep in mind that Google doesn’t just look at the anchor text itself to evaluate the relevance of your link. They also use the page as a whole and the surrounding content.
As an extreme example, if the page you’re getting a link from is about childcare but the anchor text is about electronic cigarettes, that’s going to raise some red flags.
So instead of stuffing your anchor text with keywords, try to get your link placed on pages relevant to your article and ideally have partial match or phrase keywords within the same paragraph as your link.
Let me know if you have any questions and I’ll see you next week with yet another actionable SEO strategy.
Link Reclamation and 3 Highly-Effective Link Building Tips
Welcome back to mddigitalgraphicdesigns’ weekly content series, where we give you actionable SEO strategies and tips that you can implement today and start seeing results.
While the original plan was to share one actionable SEO tip with you every week…
I’m a little too excited to share these with you so you’re going to get four from me today.
We’re going to talk about one highly effective link building strategy and three simple ways to get more out of your existing links.
Time to learn: 20 minutes
Impact (1-10): 8
Tools required: Ahrefs
Tools suggested: Archive.org
Now, let’s get to it…
Tip #1 – Link Reclamation
Just like we talked about in our broken link building guide, the internet is fickle and things can break fairly easily.
Not only do things break all the time, people change their opinions, update old content, and do all kinds of weird things that don’t necessarily make sense.
Point being? The internet changes rapidly.
Unfortunately this also means that a good chunk of your hard earned backlinks are also vanishing every single month.
The good news is that this means your competitors are also losing links but probably don’t know that these are often quite easy to recover!
P.S. While this is completely unscientific and just a gut feeling based on my observations…
I believe that when you lose links, you’re not only missing out on the lost “link juice”. You’re also getting additional negative effects because your website appears to be declining in quality.
Enter Link Reclamation – The Theory
As you’ve probably already guessed, link reclamation is the process of tracking the backlinks your site has lost and trying to recover them.
Before I show you how to find lost links…
The primary thing we’re going to have to figure out to reclaim your links is why they were removed in the first place. This’ll help us decide which angle and strategy to use.
Here are some of the most common reasons I’ve seen for links get removed AND potential angles we could take to recover them:
Page deleted on purpose – Perhaps they’ve changed their opinions on a topic or followed our content audit process to improve their rankings. Either way, they’ve decided that the page that was linking to you shouldn’t exist anymore for whatever reason and you’ll likely have a hard time convincing them otherwise.
Page deleted by accident – I don’t know about you but in the last decade, I’ve probably accidentally deleted at least 100 high performing pages by accident before my morning coffee. It happens and I’ll be super grateful if you let me know by email when you find one of these pages (and your link will be live again, too!).
How do you tell the difference between this and a page deleted on purpose? I generally check for these three things:
- Use Archive.org’s Wayback Machine to see what content used to exist on the URL. Was it a high-quality or important-looking page? If it was your site, would you have a reason to delete it?
- Use Ahrefs’ Site Explorer to see how many backlinks the page has – if there’s a decent amount, no sane webmaster (with basic SEO experience) would let the page go dead. If it has a lot of links, you could even use it as an angle to convince them to restore the page.
- Use Ahrefs’ Internal Backlinks feature to see if they are linking to this page from other pages on their site. If there’s a lot of internal links, it was probably an important page to them.
Either way – with deleted pages I always like to email the site owner from a personal (non-work) email and take a stab at getting it live again.
“Hey, I was trying to access XXX page while looking for YYY but it seems like the page doesn’t load? Do you have another link for this?”
Updated content – There’s a ton of reasons for web masters to update existing pages on their site. Not only does Google prefer up-to-date articles and fresher content, your competitors might have one-upped you and started outranking.
When we update content, we generally don’t just add a few sentences and call it a day. We look at how competitors have approached things and most likely re-do the entire page from scratch.
This means there’s a solid chance I don’t even know your link existed and doesn’t mean they don’t like you or your content. It simply didn’t come to mind for the new article.
While reclaiming the exact link won’t be possible in this case, you can treat it as a traditional outreach email.
Write a few paragraphs or sections that’d make their article better and use your own page as a source or place to refer to for additional information.
Ideally this would be the same page you had a link from in the past, but if the new page is on a different topic, you could use a different article to try and nab the link.
Competitors doing outreach – “I noticed you link to X’s article about Y. We have a similar article over at Z with fresh data from 2020 and a ton of helpful graphics. Do you think your readers might find it a more useful resource?”
If you haven’t received one of these emails yourself, you’ve probably heard us or other SEOs talk about this link building strategy.
Well, outreach link building definitely works because fairly often you’ll find your link replaced by a competitors article, likely due to an outreach email similar to the above.
Outreach links aren’t that easy to score so this is a moment to reflect on your own content – are your competitors really doing that much better that someone is willing to take time out of their day to replace an old link?
P.S. They might have also paid to place that link 🙂
In this case, you’ll likely have to either take the loss or severely update your content and try to earn it back the hard way.
I recommend the latter for a variety of reasons.
New SEO team – Sometimes the website will hire a new marketing or SEO person.
And let me tell ya… there’s nothing more frustrating than dealing with inexperienced in-house SEOs.
This may lead to odd policies such as not linking to websites under a certain domain rating, limiting the number of external links per page, and so on.
If it’s a site-wide policy they’ve decided on, your chances of changing their minds are quite slim so I generally don’t bother with these.
Page redirected – If the linking page has been redirected to another URL, it’ll be marked as a lost link by Ahrefs but this might not always be the case.
You’ll want to check for your link on the new page – perhaps they’ve simply updated the URL and the content is the same. In this case, you’ve got nothing to worry about as the link wasn’t actually lost.
If the page has been redirected to another piece of content, you’ll want to take the same approach as you would with content that has been updated.
Check to see if you have anything relevant to add to the page that would act as a reason to link to you, do the work for the site owner, and then reach out to them.
How to Actually Find Lost Links
Now that we’ve covered the primary types of lost links and how you might go about regaining them, you’re probably wondering how you’d even know which links have vanished.
Unless you’re new to these guides, you won’t be a stranger to Ahrefs and that’s exactly the tool we’re going to use today.
Head over to their Site Explorer, type in your domain, and click on “Lost” under the “Backlinks” tab.

This defaults to links lost in the last 7 days but using the calendar you can set and custom date range.
You’ll see that they also make your life just a bit easier by flagging the cause for the link being dropped – whether the link has been removed, the page deleted, redirected, etc.
Not only that, you’re able to set filters in the top menu for specific link types, minimum domain rating requirements, traffic, and so on and so forth.
As a final note – you can also use the Ahrefs Alerts feature to keep track of lost backlinks automatically in the future.
You’ll get either a daily or weekly email with all of the lost links and be able to act on them fast.
If you have any questions about this approach, don’t hesitate to drop us an email, but now on to the other two tips.
Tip #2 – Ask Existing Links to be Changed
Let’s face it.
Most website owners know very little about SEO and don’t exactly have a plan when it comes to linking to you.
You know how media sites and big publications have processes for these things?… Quotes generally link back to the exact source, company names to the website, people’s names to their social handles, etc?
Well, a lot of website owners will just toss in a link to your homepage and be done with it, even if there was a more appropriate place for it.
While high quality links pointing to anywhere on your site are a good thing, the more links you can get to a page you’re actually trying to rank, the better.
Every month we have our team go through new links and see if anyone has linked to the wrong place or if there’d be a more appropriate place.
Just recently, there was a post that mentioned our link building service but then linked to our homepage with a branded anchor instead.
We sent them an email and asked them to switch it over and they complied without any questions asked.
The same approach could be taken with your services, products, or even blog posts.
Tip #3 – Check for Dead Pages
One of the first things I like to check for when we start doing link building for clients is if they have backlinks to any 404 pages.
People with no SEO experience will not think twice about deleting a page with dozens of links and not redirecting it… We know this is a massive waste of links.
So head over to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer, look for the “Best by Links” report, and set a filter to only display 404 pages.

There’s no one single way to address this, but I’d advise you to start with the same process we described in tip #1 and figure out why you’ve deleted these pages in the first place.
Then, from there on out you can decide whether you should be restoring the page or redirecting it somewhere else.
This doesn’t make a huge difference but I’m not a huge fan of redirected links as it’s something SEOs have been abusing for close to a decade. It’s only a matter of time until Google (further) cracks down on these.
So even if you set up a redirect, if the link was legitimate, reach out to the site owner and let them know that the page is now up in a different place and ask them if they’d be able to update it on their site.
This is the same thing I recommend people do when they rebrand their site.
Sure, if you redirect to your new brand you’ll probably maintain your rankings decently but I believe Google is going to take it as a massive positive signal if these sites reinforce that by updating their links from “Old Brand and Redirect” to “New Brand”.
Tip #4 – Get Internal Links to Your Backlinks
Before we get into this one…
This is a strategy that generally works best if you’re willing to pay sites for their effort and time.
Keep in mind that this may be frowned upon by Google and it’s also not something that we condone.
Now…
The more internal links a page has, the more important it is in the eyes of Google, and the more value you’ll get from having a backlink from those pages.
It’s obviously difficult to convince someone to link to your website. But how difficult is it to convince someone to keep their visitors on their site longer, help their own content rank better, and get more traffic?
Well, it’s actually proven to be a bit more difficult than we originally thought, but it’s an effective strategy nonetheless. A lot of people will comply, but a decent chunk will also ask for money as they know you’re trying to gain something from it.
But if you’ve got the resources to add it to your toolkit, the process is quite simple.
Choose a backlink you’ve attained from a relatively large site (in terms of number of pages) and then use the “site:” search function in Google to find other pages that have covered the same topic. Then see if there’s a contextual way to link to the other article and note it down for your email.
For example, if I did a guest post on Smash Digital about keyword research, I’d do a Google search for: “site:smashdigital.com keyword research” and find every other post that could link to the guide.
If you find yourself having to convince site owners that internal links are beneficial to their site, you could send them this article